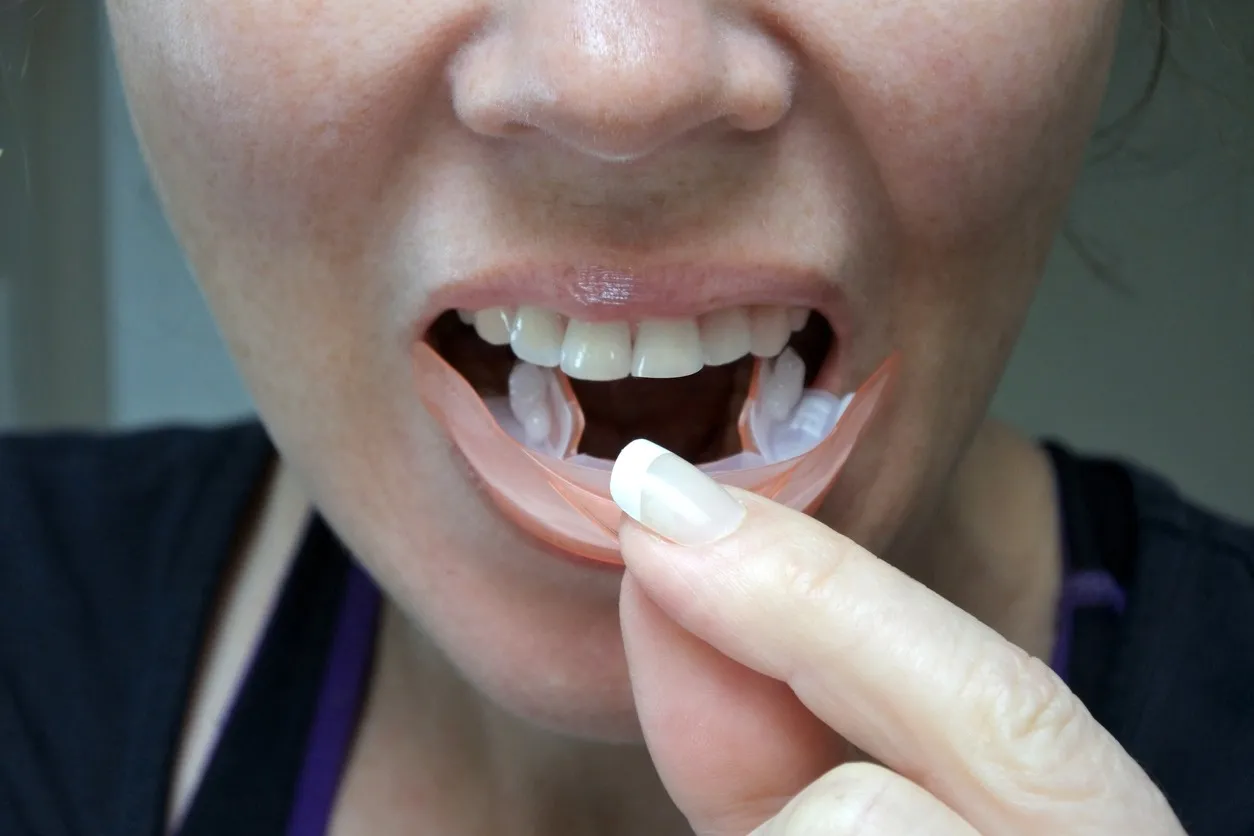
Understanding Whitening Strips
Whitening strips have become a popular and convenient method for achieving a brighter smile. But how do these thin, flexible strips actually work, and what should you know before incorporating them into your oral care routine? This article delves into the science behind whitening strips, exploring their active ingredients, the process of teeth whitening, and factors that influence their effectiveness. Understanding these elements empowers you to make informed decisions about your dental health and achieve the desired results safely and effectively. We’ll navigate through the various aspects of whitening strips, from the different types of teeth stains to the potential side effects, providing a comprehensive guide to this common cosmetic dental treatment.
How Whitening Strips Function
Whitening strips function through a chemical process designed to break down stain molecules on the surface of your teeth. They are coated with a whitening agent, typically hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. When applied to the teeth, these agents penetrate the enamel and dentin, the layers that make up your teeth, breaking down the discolored molecules. This process effectively lightens the overall shade of your teeth, resulting in a brighter smile. The effectiveness of this process depends on several factors, including the concentration of the active ingredient, the duration of application, and the type and severity of the stains present.
The Active Ingredients
The key to whitening strips’ effectiveness lies in their active ingredients. These chemicals are responsible for the bleaching action that removes stains and lightens teeth. They work by oxidizing the stain molecules, breaking them down into smaller, less visible particles. The most common active ingredients used in whitening strips are hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide. The concentration of these ingredients varies depending on the product, with higher concentrations often leading to faster, but potentially more intense, results.
The Role of Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a powerful oxidizing agent that is a common ingredient in many teeth whitening products, including whitening strips. It directly bleaches the teeth by penetrating the enamel and dentin. As hydrogen peroxide breaks down, it releases oxygen molecules that react with the stain molecules, breaking them down and making them less noticeable. The higher the concentration of hydrogen peroxide, the faster and more potent the whitening effect, but also the greater the potential for side effects like tooth sensitivity.
The Role of Other Ingredients
Besides the active whitening agents, whitening strips contain other ingredients that contribute to their overall effectiveness and safety. These can include: stabilizers, which help maintain the potency of the hydrogen peroxide; adhesive agents, which ensure the strip adheres to the teeth; and flavoring agents, which improve the taste and user experience. Some strips may also contain ingredients to reduce tooth sensitivity, such as potassium nitrate. The specific combination of ingredients varies by brand, and each plays a role in the product’s performance and how well it is tolerated by the user.
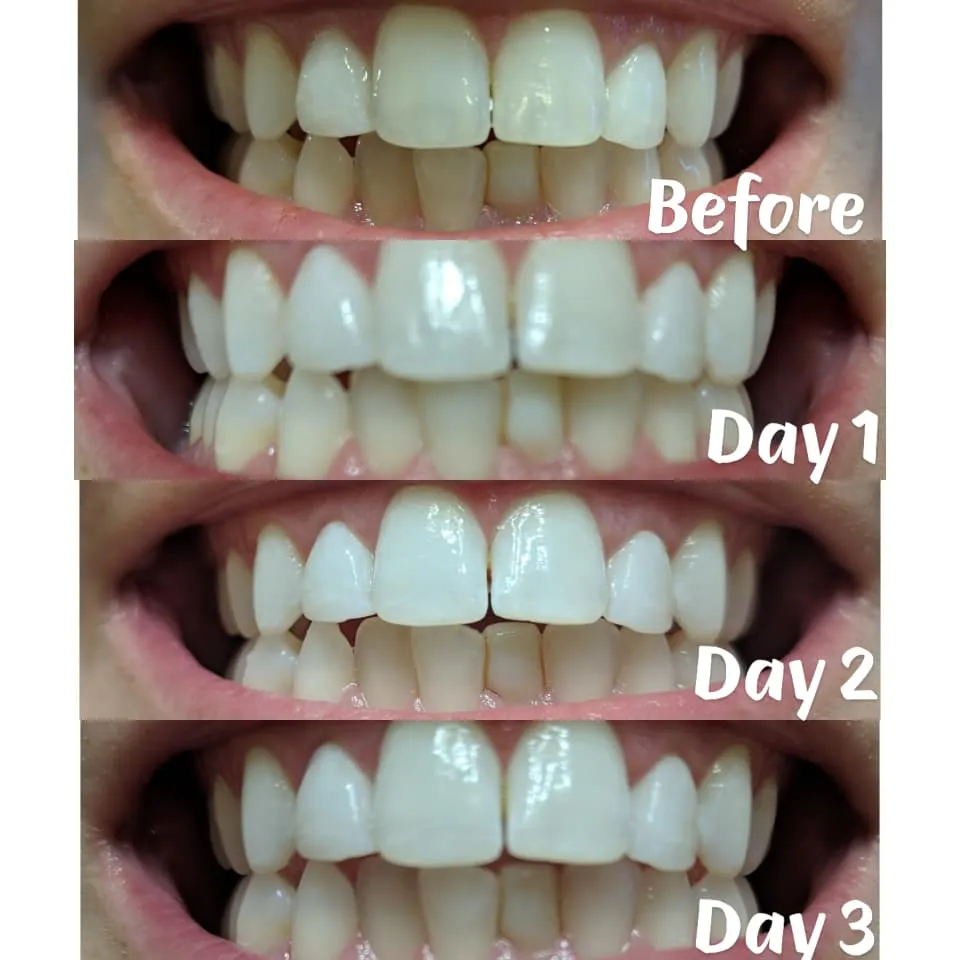
The Whitening Process Explained
The whitening process involves several steps, starting with the application of the strip to the teeth. Once applied, the whitening agent begins to penetrate the enamel. The hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide releases oxygen, which then reacts with the stain molecules. This oxidation process breaks down the larger, colored molecules into smaller, colorless ones. The duration of this process, as well as the concentration of the active ingredient, determines the degree of whitening achieved. Regular and consistent use, following the product’s instructions, is crucial for optimal results and achieving a noticeably brighter smile. It is vital to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to ensure both effectiveness and safety during the whitening process.
Teeth Staining and Discoloration
Understanding the different types of teeth stains and their causes is essential for effective whitening. Teeth can become discolored due to various factors, and knowing the source of the stains can help you choose the most appropriate whitening method. Different types of stains respond differently to whitening treatments, so this knowledge is crucial to setting realistic expectations. For example, some stains are easier to remove than others, and certain types of discoloration might not be improved by whitening strips at all. A complete assessment of teeth staining is important.
Types of Teeth Stains
Teeth stains are generally classified into two main categories: extrinsic and intrinsic. Extrinsic stains affect the surface of the tooth, primarily the enamel. These stains are often caused by the accumulation of colored substances from foods, drinks, and tobacco products. Intrinsic stains, on the other hand, originate from within the tooth, in the dentin layer. These stains can be caused by factors such as aging, genetics, certain medications, or trauma to the tooth. The approach to whitening varies significantly depending on the type of stain, with extrinsic stains typically responding more readily to whitening strips.
Extrinsic vs. Intrinsic Stains

Extrinsic stains are surface stains that adhere to the enamel of the teeth. Common causes include coffee, tea, red wine, and smoking. These stains are usually yellow or brown and tend to respond well to whitening strips because the active ingredients can directly interact with the stain molecules on the tooth’s surface. Intrinsic stains, located deeper within the tooth structure, can be more challenging to treat. They may appear as gray, blue, or even yellow, and often require more intensive whitening methods, possibly beyond the scope of whitening strips. Addressing the underlying cause of the stain is also important for long-term results.
Causes of Tooth Discoloration
Tooth discoloration can stem from a variety of causes, each influencing the type and severity of staining. Common culprits include dietary choices, habits, and natural aging processes. Understanding these causes can help in both prevention and treatment. Certain foods and beverages are notorious for staining teeth, while tobacco use significantly increases the risk of discoloration. Moreover, as we age, the enamel thins, revealing more of the underlying dentin, which tends to be more yellow, contributing to the appearance of a less white smile. Addressing these causes can help maintain a brighter smile.
Food and Drink
Certain foods and drinks contain chromogens, which are color-producing substances that can stain tooth enamel. Beverages such as coffee, tea, red wine, and dark-colored sodas are well-known for their staining properties. Additionally, deeply pigmented foods like berries, curries, and soy sauce can contribute to discoloration over time. Minimizing the consumption of these items or practicing good oral hygiene after consumption can help reduce the risk of staining. Regular brushing and flossing can help remove the chromogens before they have a chance to set into the enamel. Choosing lighter-colored alternatives can also help.
Smoking and Tobacco
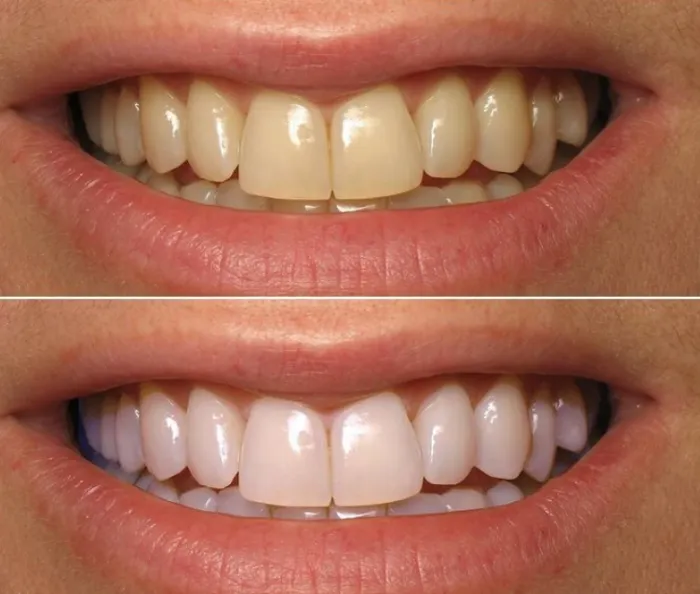
Smoking and the use of tobacco products are significant contributors to tooth discoloration. Tobacco contains nicotine and tar, which stain teeth, leading to a yellow or brown appearance. These stains are often stubborn and can be difficult to remove with regular brushing alone. Moreover, smoking and tobacco use can also impact oral health in other ways, increasing the risk of gum disease and other dental problems. Quitting tobacco use is the best way to prevent and reverse tobacco-related staining, as well as improve overall oral health. Professional teeth cleaning and whitening treatments may also be necessary to restore a brighter smile.
Aging
As we age, our teeth naturally tend to become less white. This is because the enamel, the outer protective layer of the tooth, gradually wears down over time. As the enamel thins, the underlying dentin, which is naturally more yellow, becomes more visible. This process, combined with the accumulation of stains from food and drink, contributes to the overall discoloration of teeth. Maintaining good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and professional cleanings, can help slow down the aging process on teeth and keep your smile brighter for longer. Whitening treatments can also help counteract the effects of aging and restore a more youthful appearance.
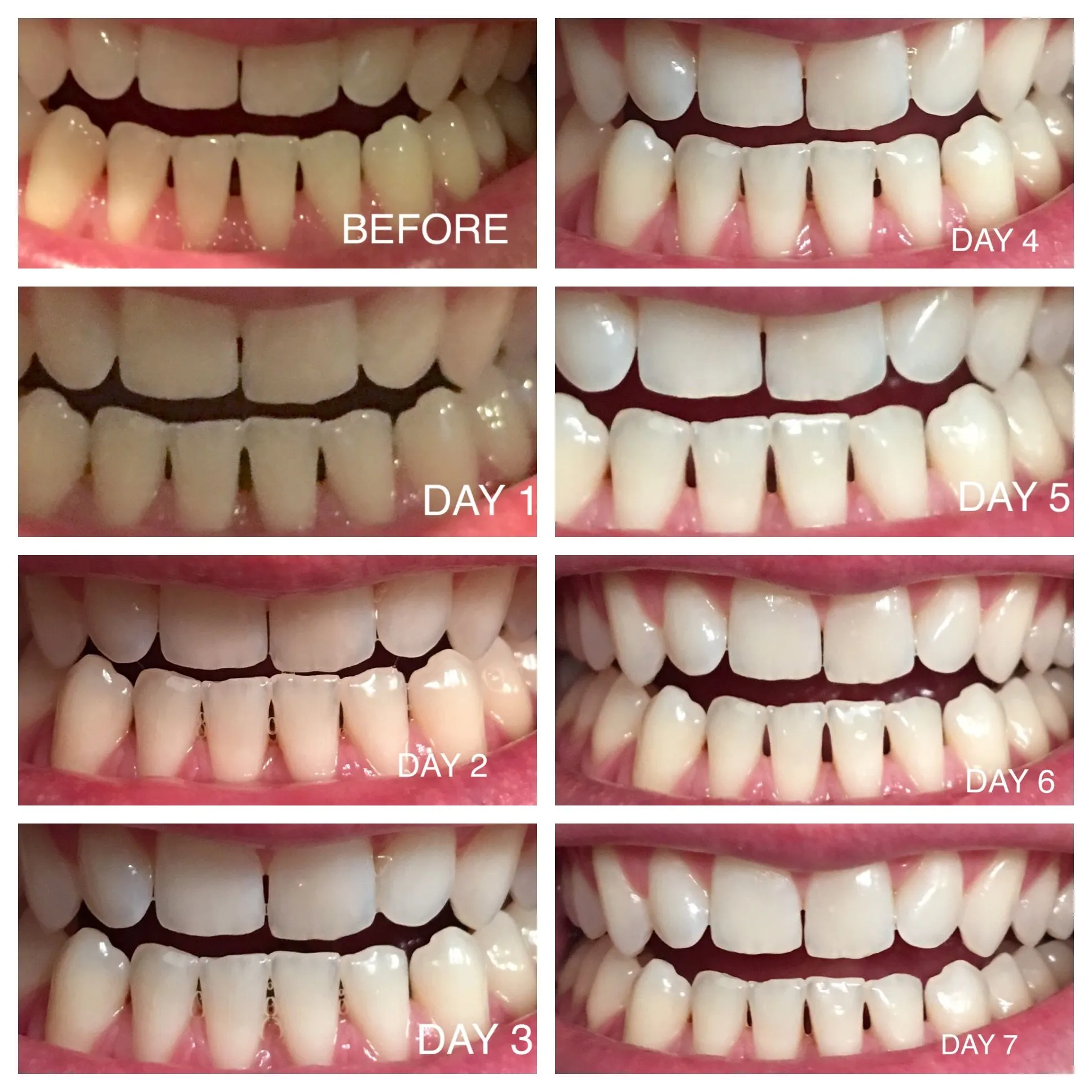
Whitening Strip Effectiveness
The effectiveness of whitening strips is influenced by several factors, including the strength of the whitening agent, the duration of use, and the user’s adherence to instructions. While whitening strips can be effective for many, the results vary based on the individual and the nature of the stains. Understanding these influencing factors can help you set realistic expectations and maximize the benefits of this popular whitening method. It is essential to remember that not all teeth are the same, and therefore, the results will differ from person to person, depending on the initial shade and the type of stains.
Factors Influencing Results
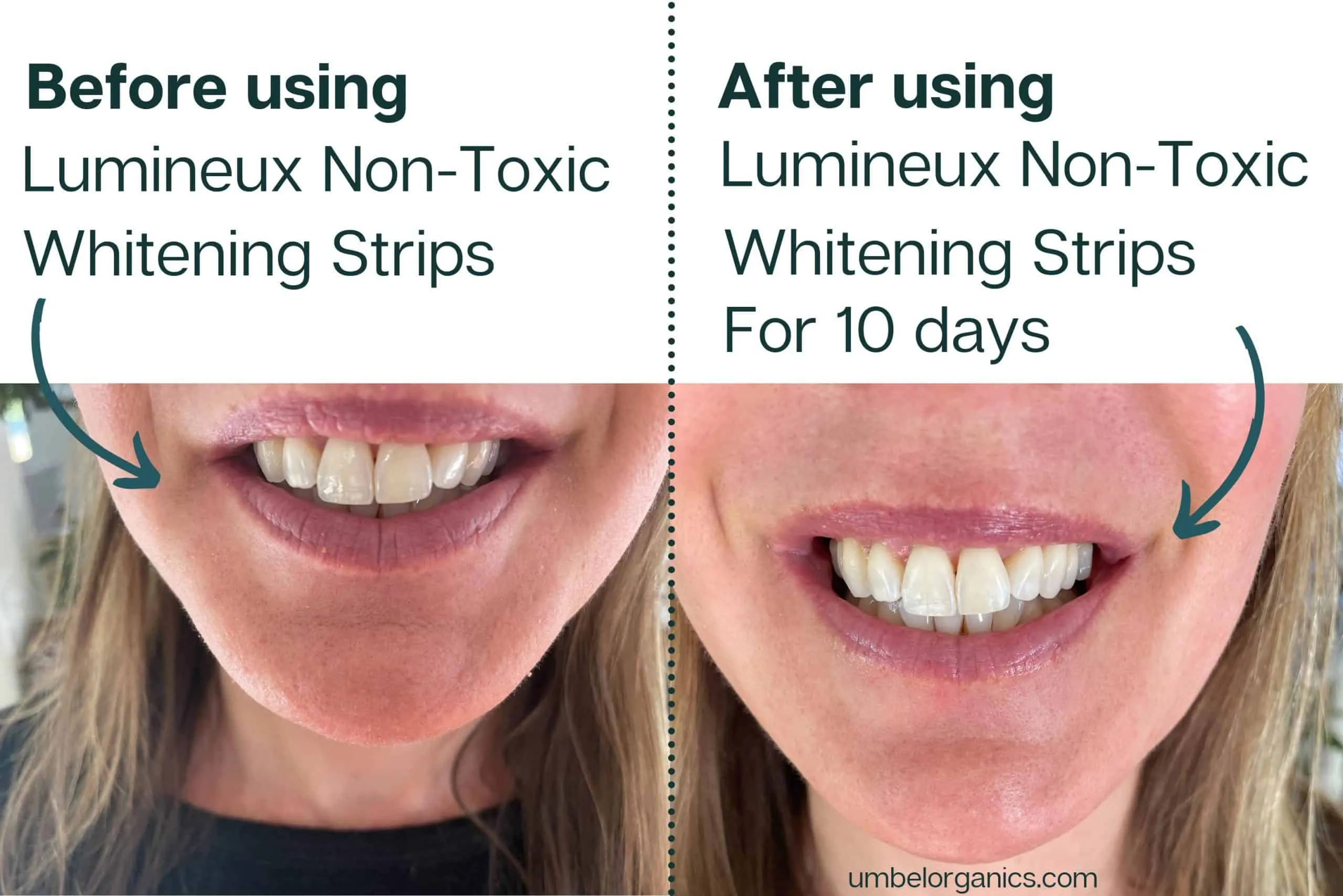
Several factors determine the effectiveness of whitening strips. The concentration of the whitening agent, usually hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, plays a significant role. Higher concentrations can lead to quicker results, but they can also increase the risk of sensitivity. The duration of use, as recommended by the product instructions, is also critical. Consistency in using the strips over the recommended period is key to achieving the desired whitening effect. Moreover, the user’s adherence to the instructions, including proper application and avoiding staining foods and drinks during treatment, significantly impacts the outcome. Following these guidelines maximizes the chance of a successful result.
Strength of the Whitening Agent
The strength, or concentration, of the whitening agent in the strips is a primary determinant of their effectiveness. Whitening strips typically contain varying percentages of hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. Higher concentrations tend to yield faster results, but they may also increase the likelihood of side effects, such as tooth sensitivity. Over-the-counter strips often have lower concentrations compared to professional treatments offered by dentists. Choosing the right strength depends on your individual needs, the severity of your stains, and your tolerance for potential side effects. If you have sensitive teeth, it is often advisable to start with a lower concentration.
Duration of Use
The duration of use, as specified by the product instructions, significantly impacts the effectiveness of whitening strips. Most whitening strips require consistent use over a set period, often ranging from several days to a few weeks, to achieve noticeable results. The duration of the treatment is carefully determined by the manufacturer, taking into account the concentration of the active ingredient and the desired level of whitening. Adhering to the recommended usage schedule is crucial. Skipping applications or shortening the treatment time may lead to less effective results. Therefore, consistency is key when using whitening strips to get the best possible outcome.
Adherence to Instructions

Strict adherence to the manufacturer’s instructions is paramount for the effective and safe use of whitening strips. This includes properly applying the strips to the teeth, avoiding contact with the gums, and following the recommended application time. Not following instructions can lead to ineffective whitening and an increased risk of side effects, such as gum irritation or tooth sensitivity. Furthermore, the instructions often recommend avoiding certain foods and beverages that can stain teeth during the treatment period. By meticulously following the guidelines, you maximize the potential for achieving a brighter smile and minimize potential risks associated with the whitening process.
Limitations of Whitening Strips
While whitening strips are an accessible and convenient option for teeth whitening, they do have limitations. They are not suitable for everyone, and their effectiveness varies depending on the type of stains and the condition of the teeth. Understanding these limitations helps manage expectations and determine if whitening strips are the right choice for you. Some types of stains are resistant to whitening strips, and certain dental work may not be affected by the treatment. In cases where these limitations exist, other professional whitening options may be more appropriate.
Not Suitable for All Types of Stains
Whitening strips are most effective on extrinsic stains, those located on the surface of the enamel. These are typically caused by food, drinks, and tobacco. However, they may be less effective on intrinsic stains, which originate from within the tooth structure. Intrinsic stains can result from factors such as aging, genetics, certain medications, or trauma. In these cases, professional whitening treatments or other dental procedures may be necessary to achieve the desired results. It’s important to know the origin of stains before investing in whitening strips, as some stains may not respond to the treatment.
Effectiveness on Dental Work
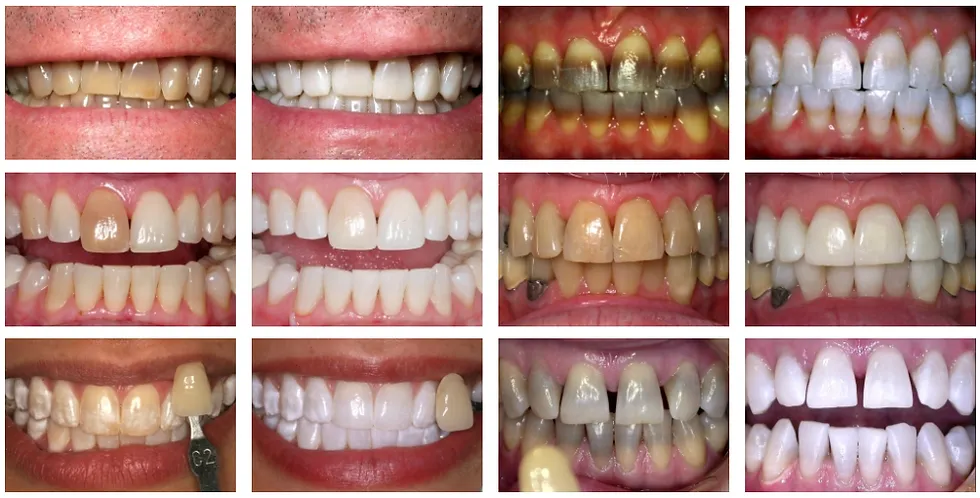
Whitening strips are designed to whiten natural teeth and are generally ineffective on dental work such as fillings, crowns, veneers, and dentures. These materials are made from different substances and do not respond to the whitening agents in the same way as natural tooth enamel. If you have dental work, whitening strips may leave the natural teeth whiter than the restorations, creating a noticeable color difference. In such cases, consulting with a dentist about alternative whitening options, such as professional whitening tailored to match the shade of your dental work, is recommended to achieve a consistent and natural-looking result. Before starting, you should address this with your dentist.
Potential Side Effects
While whitening strips are generally safe, they can cause some side effects. These are usually mild and temporary, but it’s essential to be aware of them before starting the treatment. The most common side effects are tooth sensitivity and gum irritation. The intensity of these side effects can vary depending on the individual, the concentration of the whitening agent, and how the strips are used. Understanding and recognizing these potential side effects can help you manage them effectively and decide if whitening strips are the right choice for you. If you experience severe or persistent side effects, it is important to consult your dentist.
Tooth Sensitivity
Tooth sensitivity is a common side effect of using whitening strips. The whitening agents can penetrate the enamel and reach the dentin, which contains tiny tubules that lead to the nerve of the tooth. This can cause temporary sensitivity to hot, cold, sweet, or sour foods and drinks. The degree of sensitivity varies from person to person. Some people may experience mild discomfort, while others may have more significant sensitivity. To minimize sensitivity, it’s advisable to use strips with lower concentrations of the whitening agent, apply them for shorter periods, or use sensitivity-reducing toothpaste during treatment. If sensitivity persists or becomes severe, stop using the strips and consult your dentist.
Gum Irritation
Gum irritation is another potential side effect of whitening strips. The whitening agents, such as hydrogen peroxide, can irritate the soft tissues of the gums, causing redness, swelling, or tenderness. This irritation typically occurs if the whitening agent comes into direct contact with the gums. Proper application of the strips is crucial to avoid this side effect; the strips should be applied only to the teeth and not touch the gums. If gum irritation occurs, it is best to stop using the strips and allow your gums to heal. Using a lower concentration of the whitening agent or shortening the application time can also help reduce irritation.
Proper Usage and Safety Measures
Proper usage and adherence to safety measures are essential for ensuring the effectiveness and safety of whitening strips. Incorrect application or misuse can reduce the effectiveness of the strips and increase the risk of side effects. Careful attention to the product’s instructions, including how to apply the strips, how often to use them, and when to avoid using them, can help you achieve the best possible results while minimizing potential risks. Understanding the dos and don’ts of whitening strip usage ensures a positive experience and a brighter, healthier smile. This section provides you with the key guidelines for using whitening strips effectively and safely.
Applying Whitening Strips Correctly
Correct application of whitening strips is critical for both effectiveness and safety. First, brush your teeth gently before applying the strips to remove any plaque or debris but avoid brushing immediately before. Gently peel the strips from their backing and apply the sticky side to your teeth, aligning them with your gum line. Press the strips firmly against your teeth, ensuring good contact. Fold any excess strip material behind the teeth to hold them in place. Avoid touching your gums with the whitening agent. After the recommended time, remove the strips and discard them. Rinse your mouth to remove any remaining gel. Following these steps precisely will help ensure that the whitening process is as effective as possible.
Frequency of Use
The frequency of using whitening strips depends on the specific product and your individual needs. Always follow the instructions provided with the strips. Typically, you’ll apply the strips once or twice a day for a certain period, often lasting from a few days to several weeks. Avoid overusing the strips, as this can increase the risk of side effects such as tooth sensitivity and gum irritation. If you notice any sensitivity or irritation, it is best to reduce the frequency of use or discontinue the treatment. For maintenance, you may use whitening strips periodically. Regular dental check-ups also help you stay on the right track with your oral health and whitening goals.
When to Avoid Whitening Strips
There are certain situations where you should avoid using whitening strips or consult your dentist before starting treatment. If you have sensitive teeth or gum disease, whitening strips may exacerbate these conditions. If you have dental work such as fillings, crowns, veneers, or dentures, whitening strips will not whiten these and can create a mismatch in color. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, it is generally recommended to avoid teeth whitening treatments. Additionally, if you have any existing oral health problems, such as cavities or inflamed gums, it’s best to address these issues before starting a whitening regimen. Always consult your dentist before starting any whitening treatment.
Alternatives to Whitening Strips
While whitening strips are a convenient and affordable option, several alternatives are available for those seeking to brighten their smiles. These alternatives vary in terms of effectiveness, cost, and application method. Understanding these alternatives can help you choose the best whitening solution for your individual needs and preferences. From professional treatments offered by dentists to over-the-counter options such as whitening toothpastes and gels, a wide range of choices allows you to find the most suitable path to a brighter, more confident smile. Consulting with your dentist is the best way to determine the most appropriate choice.
In summary, whitening strips are a popular and effective way to improve the appearance of your teeth. By understanding how these strips work, the types of stains they treat, and the factors that influence their effectiveness, you can make informed decisions about your oral care. While whitening strips are a convenient option, remember to follow the instructions, consider potential side effects, and consult with a dentist to ensure a safe and successful whitening experience. With careful consideration and proper use, you can achieve a brighter, more confident smile.